Breather membranes for buildings
Damp in buildings can cause a number of serious problems, such as:
- Damp patches.
- Mould growth, mildew, salts, staining and ‘tide marks’.
- Damage to surface finishes.
- Corrosion and decay of building fabric.
- Slip hazards.
- Frost damage.
- Poor performance of insulation.
- Damage to equipment, or electrical failure.
The most common causes of persistent damp in buildings are:
- Surface condensation.
- Interstitial condensation (condensation within the fabric of a building's construction, either on the surfaces of components that make up the fabric, or sometimes within the components themselves).
- Penetrating damp.
- Rising damp.
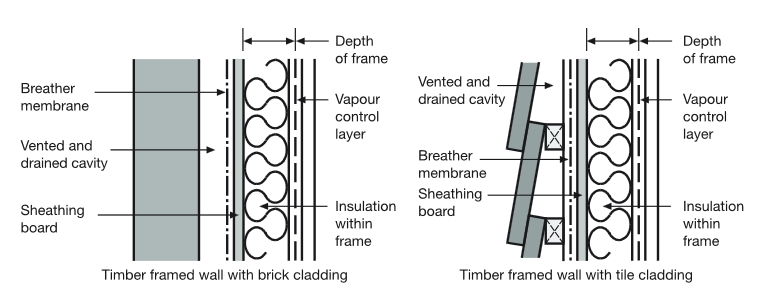
Breather membranes (or breathable membranes) are water resistant but vapour permeable. Typically they are used within external wall and roof constructions where the external cladding may not be completely water-tight or moisture resistant, such as in tiled roofs or framed wall constructions.
The membrane is located on the cold side of insulation and prevents moisture (as well as snow, wind, and contaminants such as dust) that may have been driven through the external cladding, from penetrating further into the structure. However, their air-permeability allows the structure to be ventilated, avoiding the build-up of interstitial condensation.
Any moisture that forms on the outside face of the membrane should be able to vent or drain to the outside.
Breather membranes can also improve the thermal efficiency of a building’s external envelope and can provide temporary protection from the weather during construction or repair works.
Generally, breathable membranes for wall constructions do not have to be as high a specification as those in roof constructions. In roofs, breathable membranes are required to resist wind uplift so that tiles are not dislodged by movement of the membrane.
In framed wall constructions, breathable membranes may sometimes be fitted during the manufacturing process, off site. Typically, wall constructions will also include a vapour barrier, on the warm side of insulation which prevents humid air from inside the building being driven to a point in the wall structure where it reaches its dew-point temperature and moisture condenses.
In roof constructions, breathable membranes may be supported or unsupported. The channel between fixings can be used to drain moisture to the eaves. Some breathable membranes have sufficient air-permeability that eaves and ridge ventilation of the roof is not necessary.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Infrastructure that connect the physical and digital domains.
Harnessing robotics and AI in challenging environments
The key to nuclear decommissioning and fusion engineering.
BSRIA announces Lisa Ashworth as new CEO
Tasked with furthering BSRIA’s impressive growth ambitions.
Public buildings get half a million energy efficiency boost
£557 million to switch to cleaner heating and save on energy.
CIOB launches pre-election manifesto
Outlining potential future policies for the next government.
Grenfell Tower Inquiry announcement
Phase 2 hearings come to a close and the final report due in September.
Progress from Parts L, F and O: A whitepaper, one year on.
A replicated study to understand the opinion of practitioners.
ECA announces new president 2024
Electrical engineer and business leader Stuart Smith.
A distinct type of countryside that should be celebrated.
Should Part O be extended to existing buildings?
EAC brands heatwave adaptation a missed opportunity.
Definition of Statutory in workplace and facilities management
Established by IWFM, BESA, CIBSE and BSRIA.
Tackling the transition from traditional heating systems
59% lack the necessary information and confidence to switch.
The general election and the construction industry
As PM, Rishi Sunak announces July 4 date for an election.
Eco apprenticeships continue help grow green workforce
A year after being recognised at the King's coronation.
Permitted development rights for agricultural buildings
The changes coming into effect as of May 21, 2024.






















Comments
It would be great to have a breakdown of the different types of breather membranes, in particular the difference between microporous and monolithic membranes.