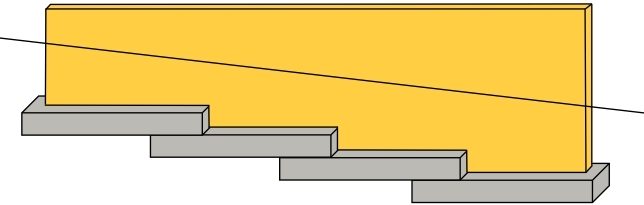
Stepped foundation
Foundations provide support for structures, transferring their load to layers of soil or rock that have sufficient bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics.
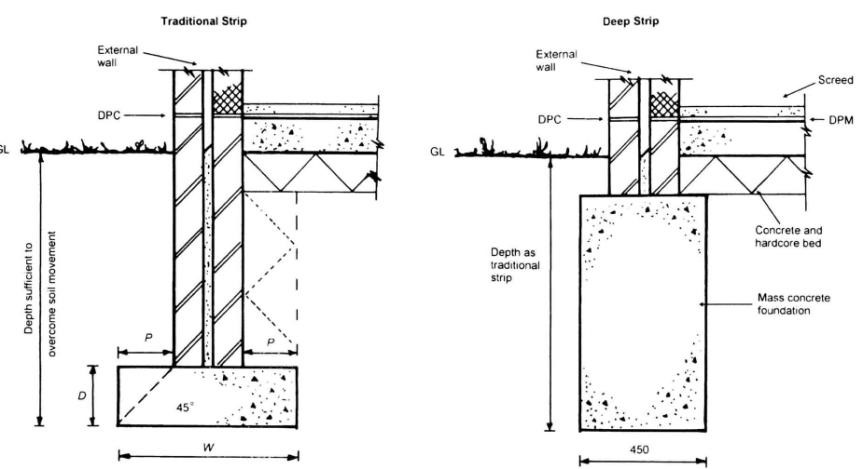
Strip foundations (or strip footings) are a type of shallow foundation used to provide a continuous, level (or sometimes stepped) strip of support to a linear structure such as a wall or closely-spaced rows of columns built centrally above them.
Where the natural surface of the ground is sloped, the most economical solution may be a stepped foundation. In this case, the foundation takes the form of a series of concrete horizontal steps following the slope of the ground.
This helps to minimise the amount of excavation and below-ground wall construction that would otherwise be required. Stepped foundations can also be used to transition from deep foundations to shallow foundations, and at corners and intersections.
Regularly stepping foundations also avoids abrupt and excessive changes in level that could cause a weakness resulting in movement. Similarly, abrupt and excessive changes in foundation depths should be avoided at corners and intersections by the introduction of stepping.
Each step in the foundation should be no higher than the thickness of the foundation. The foundation at the higher level should also overlap the lower foundation, typically by at least twice the height of the step, or by the thickness of the foundation, or by at least 300 mm (whichever is greatest).
Drainage must be carefully designed to eliminate the danger of instability due to accumulating water pressure.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Infrastructure that connect the physical and digital domains.
Harnessing robotics and AI in challenging environments
The key to nuclear decommissioning and fusion engineering.
BSRIA announces Lisa Ashworth as new CEO
Tasked with furthering BSRIA’s impressive growth ambitions.
Public buildings get half a million energy efficiency boost
£557 million to switch to cleaner heating and save on energy.
CIOB launches pre-election manifesto
Outlining potential future policies for the next government.
Grenfell Tower Inquiry announcement
Phase 2 hearings come to a close and the final report due in September.
Progress from Parts L, F and O: A whitepaper, one year on.
A replicated study to understand the opinion of practitioners.
ECA announces new president 2024
Electrical engineer and business leader Stuart Smith.
A distinct type of countryside that should be celebrated.
Should Part O be extended to existing buildings?
EAC brands heatwave adaptation a missed opportunity.
Definition of Statutory in workplace and facilities management
Established by IWFM, BESA, CIBSE and BSRIA.
Tackling the transition from traditional heating systems
59% lack the necessary information and confidence to switch.
The general election and the construction industry
As PM, Rishi Sunak announces July 4 date for an election.
Eco apprenticeships continue help grow green workforce
A year after being recognised at the King's coronation.
Permitted development rights for agricultural buildings
The changes coming into effect as of May 21, 2024.






















Comments
What are the rebar design standards for stepped footing rebar?
are 90 degree hooks at step down acceptable?